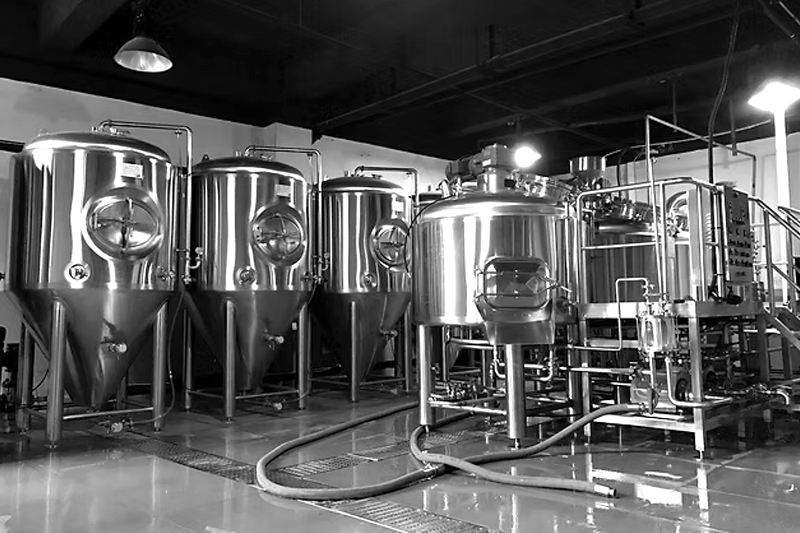
Micro brewery systems are increasingly becoming an ideal choice for craft beer lovers, small bars, and start-up breweries. A high-quality micro brewery system can not only ensure the efficiency and stability of the brewing process but also bring long-term advantages in flavor control, scalability, cleaning, and maintenance. Faced with numerous models on the market, choosing a system that truly suits their needs has become a significant concern for many brewing entrepreneurs and investors. This article will systematically analyze the micro brewery system from aspects such as equipment composition, equipment model, ease of operation, and budget control.
Table of Contents
What is a micro brewery system?
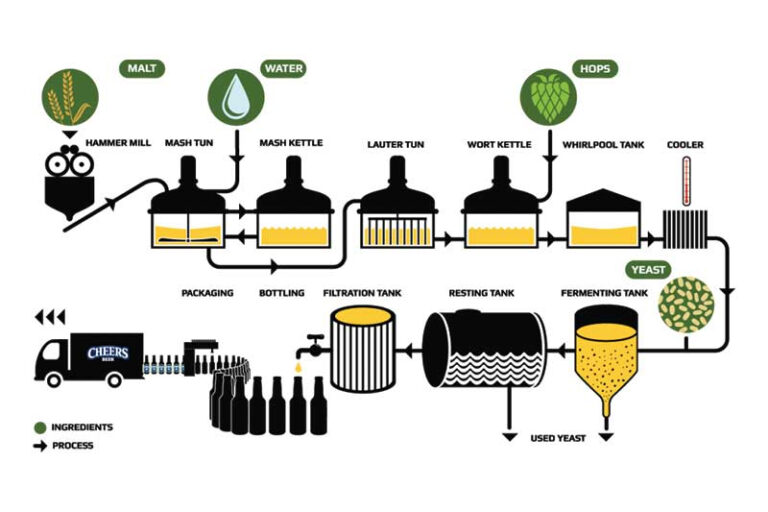
A micro brewery system usually refers to a small beer production line with an output between 100L and 2000L, suitable for small breweries, craft beer bars, restaurant chains, and craft beer entrepreneurs. It is compact, efficient, easy to operate, and flexible to adapt. It can realize the complete process of malt mash, boiling, fermentation, refrigeration, filling, etc., and is an ideal choice for handcrafted craft beer.
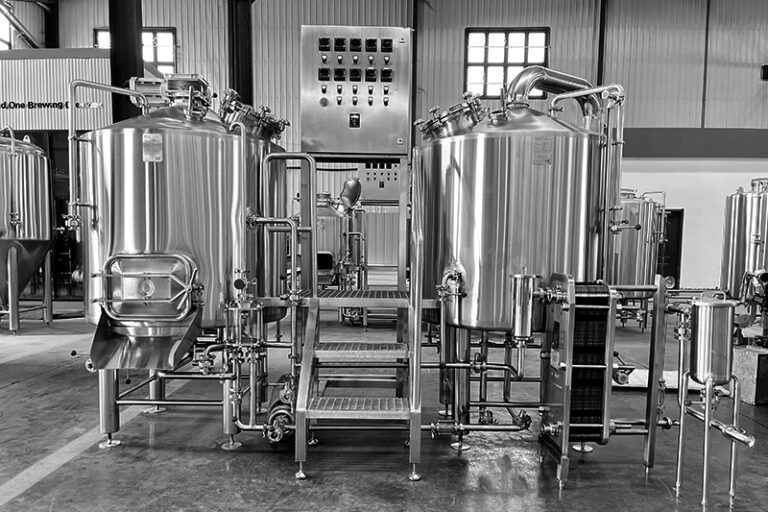

Key components of micro brewery system
Malt Mill
The malt mill is the first step in the beer brewing process. Its core function is to grind the dry malt into coarse particles suitable for mash. The appropriate degree of grinding can ensure the integrity of the husk, which is conducive to subsequent filtration while releasing enough starch for mash conversion. A high-quality grinding system can also effectively reduce dust and improve the cleanliness of the operation.
Mash/Lauter Tun
The mash tun is responsible for heating the crushed malt in water and converting it into maltose to form wort; while the lauter tun is used to separate the wort from the insoluble spent grains. A good temperature control system is the key to ensuring accurate mash and stable flavor.
Kettle & Whirlpool Tank
In the kettle tank, the wort is boiled at a high temperature to inactivate enzymes and kill bacteria, and hops are added at different times to extract bitter and aromatic components before entering the whirlpool tank.
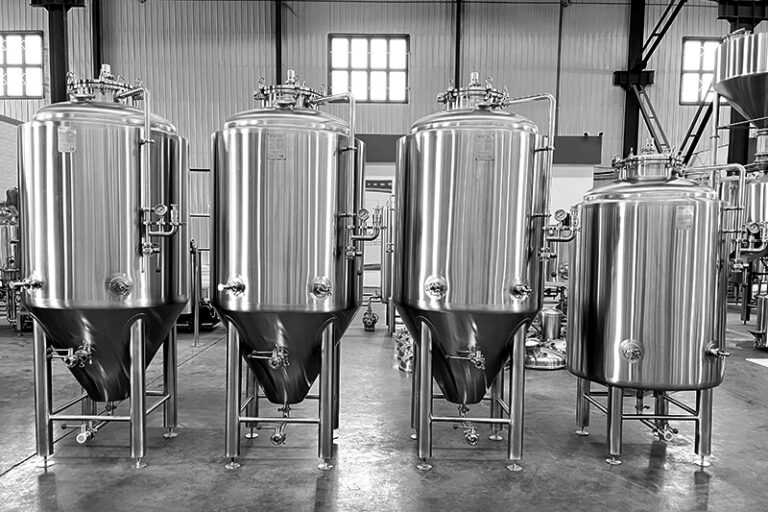
Fermentation Tank & Bright Tank
The fermentation tank is a key container for converting wort into beer. It is usually a stainless steel tank with a conical bottom, equipped with precise temperature control, a cooling jacket, a pressure regulating valve, and a CIP cleaning system. Constant temperature fermentation can ensure yeast activity and fermentation consistency, while the Bright Tank is mainly used for clarification and carbonation of finished beer, which is an intermediate link before bottling or draft beer packaging. For commercial brewers, this combination improves production flexibility and finished product quality.
Glycol Chiller
The cooling system is mainly used to control the temperature during the fermentation process. When selecting a model, the required cooling capacity should be evaluated based on the number and volume of the fermentation tanks and the brewing plan to ensure that sufficient cooling can be provided when there is a high load or when multiple tanks are fermenting at the same time.
CIP System
The CIP System can realize online automatic cleaning of pipelines and tank inner walls to ensure that the brewing system is sterile and pollution-free. With the automatic control panel, especially PLC control, it can realize one-button process setting, real-time data monitoring, abnormal alarm, and operation record storage, greatly improving production efficiency and process stability.
How to choose the best micro brewery system?
Before choosing a micro-brewing system, you need to clarify your needs and preferences:
Brewing type and purpose
Different brewing purposes require different equipment. Do you want to brew beer, wine, or cider? The process of each beverage is different, and the equipment is also different.
- Beer brewing: usually requires fermentation tanks, brewhouse equipment, and temperature control devices.
- Wine: requires equipment with a pressing function to facilitate the extraction of juice.
- Multi-functional system: can meet the brewing needs of a variety of beverages, suitable for diverse enthusiasts.
Equipment scale and capacity
capacity | Suitable for | Daily Output | Area | Recommended scenarios |
100L-200L | Entrepreneurs | 1-2 barrels | <20㎡ | Craft beer bar, mobile brewing car |
300L-500L | Small catering | 2-4 barrels | 30-50㎡ | Restaurant brewing, community brewery |
1000L-1500L | Small winery | 4-10 barrels | >70㎡ | Local brands, craft beer suppliers |
2000L and above | Mature Enterprises | More than 10 barrels | >120㎡ | Regional distribution, export business |
Ease of operation
Beginners should choose a system that is easy to operate and comes with detailed instructions;
Experienced winemakers can consider professional equipment with more comprehensive functions and adjustable parameters.
Equipment materials and quality
High-quality materials ensure the safety and hygiene of the brewing process. Common materials include:
- Stainless steel: corrosion-resistant, easy to clean, and hygienic.
- Glass: easy to observe, suitable for the fermentation stage, but fragile.
- Plastic: light and affordable, but it needs to be confirmed that it does not contain harmful substances.
Price budget
Prices range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars. Consider your budget and choose a device that is cost-effective and has the functions you need.

Automated Brewing System vs Manual System: How to Choose?
type | Advantages | Target Customers |
Manual system | Low cost, flexible operation, suitable for personalized operation | Small restaurant/individual winemaker |
Semi-automatic system | Easy operation, low error rate, high degree of standardization | Small craft brewery/laboratory |
Fully automatic system | High efficiency, intelligent management, suitable for large-scale batch production | Capacity-based brand winery |
Equipment recommendations for different customer types
Customer Type | Recommended capacity | Recommended Configuration | illustrate |
Restaurant/Bar | 100L~300L | Electric heating mash tun + 2 fermentation tanks + chiller + manual control panel | Suitable for on-site display, compact space |
Craft Brewing Studio | 300L~500L | Steam heating + multi-tank configuration + automatic control | Can develop multiple styles of beer |
Teaching/R&D Base | 100L~200L | Flexible modular system + data acquisition function | Suitable for teaching and experiments |
Small winery | 500L~1000L | Fully automatic brewhouse system + CIP + filling line | Supporting commercial distribution and growth |

FAQ
What is a micro brewing system? Who is it suitable for?
A micro brewery system refers to small beer brewing equipment with a production scale between 100L and 1000L. It is suitable for users such as craft beer halls, start-up craft brands, experimental brewing projects, and educational training institutions. It has the characteristics of small size, flexible operation, and easy control.
Can the microsystem be upgraded to a larger capacity?
Some modular systems are expandable, such as increasing the capacity of the fermentation tank, but the core control system and infrastructure need to reserve interfaces.
Are coolers and boilers required?
Yes, it is recommended to use steam boilers or electric heating systems for the mash/boiling process, and fermentation and wort cooling rely on coolers.
Can it be customized according to my space or recipe?
Yes. Most equipment manufacturers provide services such as size customization, process optimization, and equipment layout design to adapt to different venues and personalized brewing needs.
Does the micro brewery system choose electric heating, steam heating, or direct fire heating?
- Electric heating: suitable for small scale, easy installation, low initial cost;
- Steam heating: high efficiency, precise temperature control, suitable for medium scale, boiler required;
- Direct fire heating: simple structure, suitable for areas with limited budget, but relatively low thermal efficiency.
What cleaning work is required for a microbrewery system?
- Thoroughly rinse the mash tun, lauter tun, and fermentation tank after each brewing;
- Use CIP system for alkaline and acid washing to descale;
- Clean the filter plate, pump body, hose, and valve connection;
- Regularly use hot water circulation disinfection to prevent microbial contamination.
How often does the fermentation tank need to be deeply cleaned?
It is generally recommended to clean it immediately after each batch of fermentation; if it is used in multiple batches continuously, it is recommended to perform a thorough CIP cleaning + high temperature sterilization every 5-7 days.

